Temporary table is very useful tool in SQL Server for developer. It provided short term use of data. These tables can be created at runtime and can do the all kinds of operations that one normal table can do. But, based on the table types, the scope is limited. These tables are created inside tempdb database. There are two types of temporary table in SQL Server:
1. Local
2. Global
Local : Local temporary tables are only available to the current connection to the database for the current user. These are dropped automatically when the connection is closed.
Temporary tables are tables that are available only to the session that created them.
These tables are automatically destroyed at the termination of the procedure or session that created them.
Use of temporary tables in MS SQL Server is more developer friendly and they are widely used in development. Local temporary tables are visible only in the current session.
Temporary tables are created using the same syntax as a CREATE TABLE except the table name starts with a '#' sign. When the table consists of a single '#' sign, it is defined as a local temporary table and it's scope is limited to the session it is created in.
Global : Global temporary tables are available to all connections that created and exist to that database. These are dropped when the last connection using it is closed.
Global Temporary tables are visible to or available across all sessions. And all users.
Global Temporary tables are created using the same syntax as a CREATE TABLE except the table name starts with "##" (two '#' signs). When the table is only "##", it is defined as a local global temporary table and it's scope is not limited to the session it is created in.
A Global Temporary table is dropped automatically when the last session using the temporary table has completed.
Both the local temporary tables and global temporary tables are physical.
How to create Temporary Tables?
Temporary tables can be created like any table in SQL Server with a CREATE TABLE or SELECT..INTO statement.
To make the table as local temporary table, attach (#) as prefix with the name of the table.
To make the table as global temporary table, attach (##) as prefix with the name of the table.
Create Local Temporary Table using Create Table statement.
Code :
CREATE TABLE #TempTable1
(
tempfield1 INT,
tempfield2 VARCHAR(50)
)
Create Local Temporary Table using SELECT ... INTO statement.
Code :
SELECT
tempfield1 as id,
tempfield2 as Name
INTO #TempTable1 FROM ActualTable1
Above sample codes will create a local temporary table named #TempTable1 with two fields with name tempfield1 and tempfield2.
Create Global Temporary Table using Create Table statement.
Code :
--replace # to ##
CREATE TABLE ##TempTable1
(
tempfield1 INT,
tempfield2 VARCHAR(50)
)
Create Global Temporary Table using SELECT ... INTO statement.
Code :
SELECT
tempfield1 as id,
tempfield2 as Name
INTO ##TempTable1 FROM ActualTable1
How to check if Temporary table exist?
use below stored procedure for checking local temp table:
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#TempTable1') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
PRINT '#TempTable1 exists'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT '#TempTable1 does not exist'
END
use below code for checking global TempTable1 table :
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##TempTable1') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
PRINT '##TempTable1 exists'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT '##TempTable1 does not exist'
END
Uses of Temporary Tables:
A Temporary Table variable can be very useful when used with stored procedures to pass input/output parameters or to store the result of a table valued function.
Now to create the Temporary table the query will be:CREATE TABLE #TEMPTABLE(Id INT,Name VARCHAR(30),Date DATETIME DEFAULT GETDATE())
Run the query. After that the "TEMPTABLE" will be created.
Now we are going to insert some values into the TempTable.INSERT INTO #TEMPTABLE(Id, Name) VALUES(1,'shirsendu');INSERT INTO #TEMPTABLE(Id, Name) VALUES(2,'Sarnali');INSERT INTO #TEMPTABLE(Id, Name) VALUES(3,'Mrinal');
Execute the Query
Now to see the values inserted into the temp table execute the following query:select * from #TEMPTABLE
The result will look like
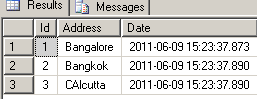
Now to create the Global Temporary Table.
For creating the table we already know to use "##" before the table name.CREATE TABLE ##GLOBALTEMPTABLE(Id INT,Address VARCHAR(30),Date DATETIME DEFAULT GETDATE())
Run the query. After that the "GLOBALTEMPTABLE" is created.
Now we are going to insert some values into the GLOBALTEMPTABLE.INSERT INTO ##GLOBALTEMPTABLE(Id, Address) VALUES(1,'Bangalore');INSERT INTO ##GLOBALTEMPTABLE(Id, Address) VALUES(2,'Bangkok');INSERT INTO ##GLOBALTEMPTABLE(Id, Address) VALUES(3,'CAlcutta');
Now to see the values inserted into the GLOBALTEMPTABLE execute the following query.select * from ##GLOBALTEMPTABLE
The result will look like:
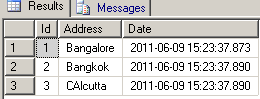
Now you can cross join between the Temporary table and the GlobalTemporaryTable as in:select * from ##GLOBALTEMPTABLE,#TEMPTABLE
The result will look like:
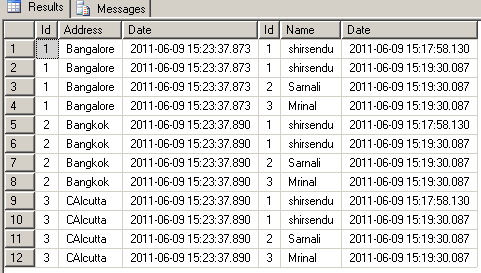
No comments:
Post a Comment